Description:
We present a new combination drug for the pharmaceutical treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) based on our discovery of a novel mechanism of hippocampal vulnerability in AD patients. Hippocampal synaptic injury and neurodegeneration are defining pathological features of the cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Current therapeutic efforts for the treatment of AD are not effective in correcting hippocampal synaptic deficits.
Our research has revealed an important contribution of GHSR1a, the functional isoform of GHSR, in the regulation of hippocampal synaptic plasticity and memory consolidation. GHSR1a heteromerizes with the dopamine receptor D1 (DRD1), thus regulating DRD1-mediated modulation of synaptic plasticity. We show that the co-activation of GHSR1 and DRD1 with their combined selective agonists rescue hippocampal synaptic function and cognition in a mouse model mimicking AD brain amyloidopathy with replicated hippocampal synaptic stress and cognitive impairment. Importantly, the two types of agonists should be mixed in an optimized ratio to achieve the best efficacy and minimize the potential side-effects.
Value Proposition:
This novel pharmaceutical approach is ready to move quickly through clinical trials as it uses clinically approved compounds and has shown great effectiveness in treating/preventing AD-related mechanisms.
Key Benefits:
- A novel disease-modifying therapy: High potential for both preventing and mitigating symptoms of sporadic and familial Alzheimer’s disease. Directly targets key molecular mechanisms causing disease-associated hippocampal synaptic failure.
- Compatibility with other medications: Anticipated to have synergistic effects with conventional medications targeting cholinesterase and glutamate receptor as well as Aβ-targeting therapies under clinical testing.
- Clinical Trial Ready: At least one agonist of GHSR1a tested in our trials, Ibutamoren (MK-0677), is approved as an investigational new compound. Several DRD1 agonists are approved for use in clinical trials.
- Tested safety: The safety of the repurposed agents has been demonstrated in previous clinical trials.
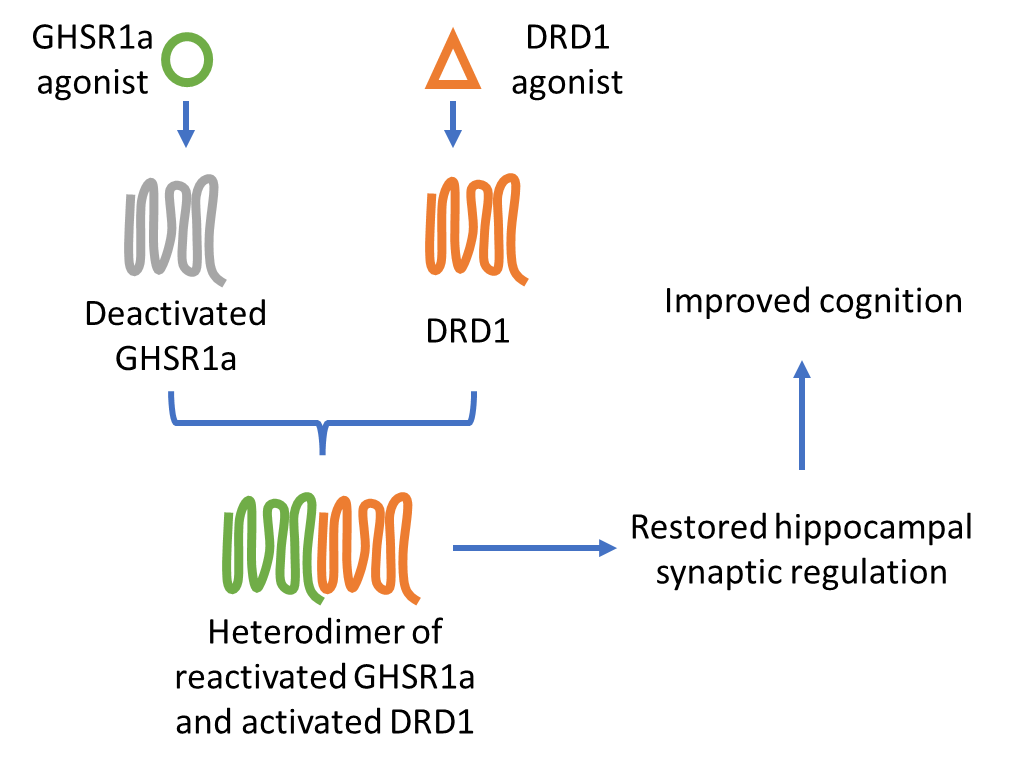
Schematic: In AD, GHSR1a is deactivated and loses capacity to heterodimerize with DRD1 for the regulation of hippocampal synaptic activity. Simultaneous application of GHSR1a and DRD1 agonists rescues GHSR1a activity, promotes GHSR1a/DRD1 heterodimers, and restores hippocampal synaptic regulation, improving cognition in patients.
|
Applications:
- Preventive and therapeutic treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease
- Therapeutic treatment of hippocampal synaptic deficits.
- Reversal of cognitive impairment
IP Status: Filed/Pending: PCT/US2020/046062
Primary Inventor: Heng Du
Contact: otc@utdallas.edu
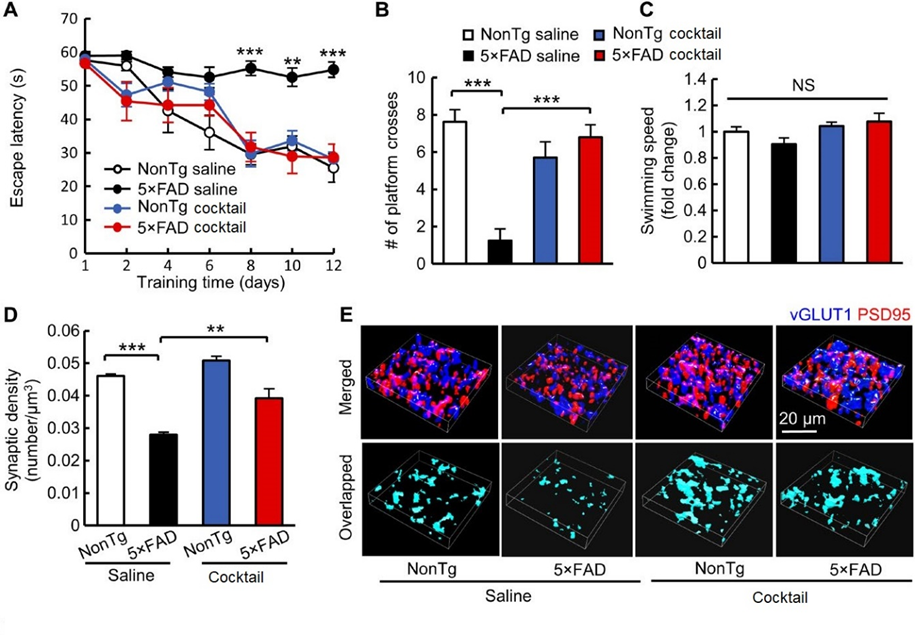
Combined Ghsr1/Drd1 activation protects hippocampal synapse and cognition in vivo. (A to C) Spatial navigation analysis in four groups of mice treated with vehicle (saline) or treated with GHSR1/DRD1 (cocktail) performing the Morris water maze test for AD impaired mice (5xFAD) and unimpaired mice (nonTg). (A) Spatial learning test showing 5×FAD cocktail versus other groups; (B) Spatial reference memory test showing 5×FAD cocktail versus other groups; (C) Swimming speed test showing 5×FAD cocktail versus other groups; D) and E) Analysis of synaptic density in the hippocampal CA1 region. 5×FAD saline versus other groups; (E) Representative 3D reconstructed images of synapse staining in the CA1 region. vGLUT1 (blue) and PSD95 (red) were used to visualize pre- and postsynaptic components, respectively. The overlaid staining of vGLUT1 and PSD95 indicates synapses.
Additional Information:
“Disrupted hippocampal growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1α interaction with dopamine receptor D1 plays a role in Alzheimer's disease” (DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aav6278)